AbstractCytokine-targeted therapy has generated a paradigm shift in the treatment of several immune-mediated diseases. Interleukin-6 (IL-6), which was initially identified as B-cell stimulatory factor 2, is a prototypical cytokine with wide-ranging biological effects on immune cells such as B and T cells, on hepatocytes, hematopoietic cells, vascular endothelial cells and on many others. IL-6 is thus crucially involved in the regulation of immune responses, hematopoiesis and inflammation. When infections and tissue injuries occur, IL-6 is promptly synthesized and performs a protective role in host defense against such stresses and traumas. However, excessive production of IL-6 during this emergent process induces potentially fatal complications, including systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), and dysregulated, persistently high expression of IL-6 causes the onset or development of various chronic immune-mediated disorders. For these reasons, IL-6 blockade was expected to become a novel therapeutic strategy for various diseases characterized by IL-6 overproduction. Indeed, worldwide clinical trials of tocilizumab, a humanized anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody, have successfully proved its outstanding efficacy against rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis and Castleman disease, leading to the approval of tocilizumab for the treatment of these diseases. Moreover, various reports regarding off-label use of tocilizumab strongly suggest that it will be widely applicable for acute, severe complications such as SIRS and cytokine-release syndrome and other refractory chronic immune-mediated diseases.
Via Krishan Maggon


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...



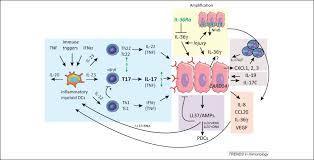






Int. Immunol. (2015) 27 (1): 21-29 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxu081