
We are delighted to announce that our paper "Maximizing MRNA Vaccine Production with Bayesian Optimization" has been recognised by Wiley as one of the most downloaded papers in Biotechnology and Bioengineering!
The paper steams from a collaboration between researchers from IBB (Sara Rosa, Miguel Prazeres and Ana Azevedo), UCL (Marco Marques) and FCUL/LASIGE (David Nunes and Luis Antunes), and explores the innovative use of machine learning, specifically Bayesian optimisation, to advance the field of mRNA production.
This award is testament to the dedication and hard work of the team, as we continue to drive innovation and make significant contributions to the field of biotechnology.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...

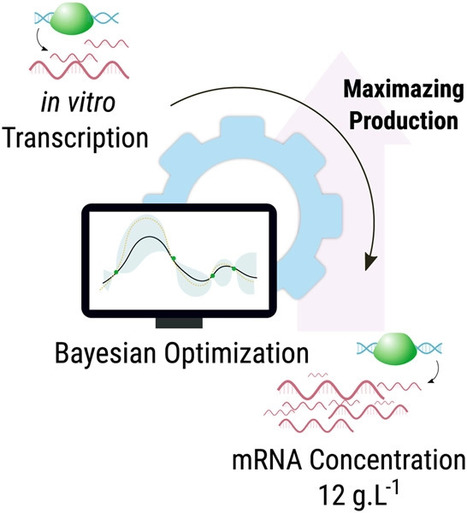
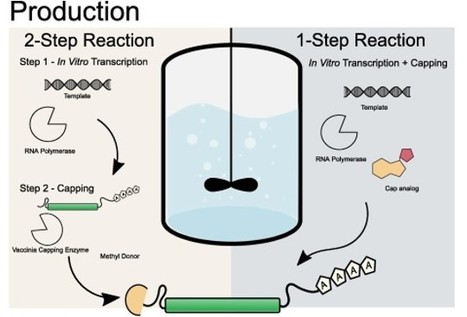
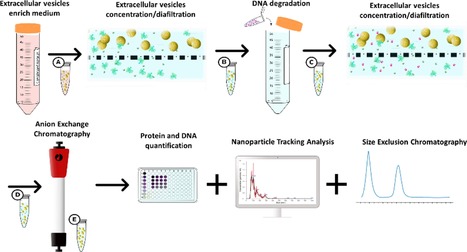
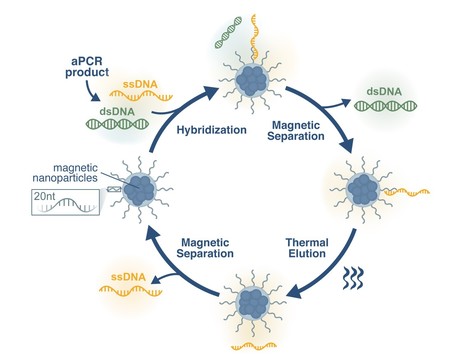





Check the award-winning paper here.