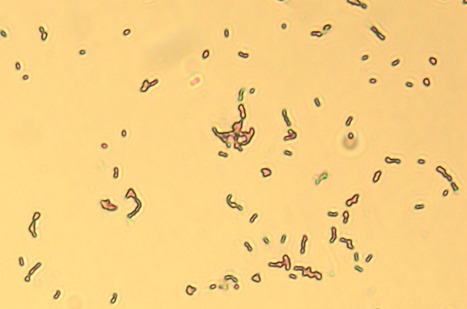
Lactococcus lactis is a food-grade, and generally recognized as safe, bacterium, which making it ideal for producing plasmid DNA (pDNA) or recombinant proteins for industrial or pharmaceutical applications. A paper published in Microorganisms by Sofia Duarte and Gabriel Monteiro from BERG-iBB reviews the major findings from L. lactis transcriptome and proteome studies, with an overexpression of native or recombinant proteins. These studies provide important insights on how to engineer the plasmid vectors and/or the strains in order to achieve high pDNA or recombinant proteins yields, with high quality standards.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...







