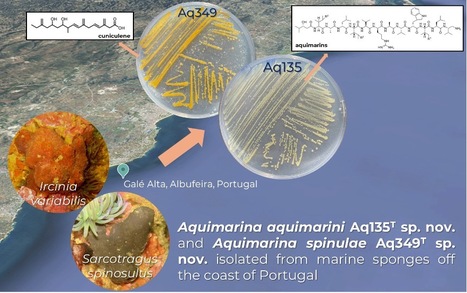
The marine bacterial genus Aquimarina (Flavobacteriaceae, Bacteroidota) receives increased attention due to its versatile natural product biosynthesis capacity and antimicrobial activities. iBB and DBE researchers Joana Couceiro,Matilde Marques, Sandra Silva, Tina Keller-Costa and Rodrigo Costa identified two novel Aquimarina species, Aquimarina aquimarini Aq135T and Aquimarina spinulae Aq349T, isolated from marine sponges in Portugal, and describe them in the International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. Aq135T is known for its production of a unique set of peptide antibiotics, aquimarins, while Aq349T is known to produce the trans-AT polyketide cuniculene. In their polyphasic approach, the researchers used phylogenetic, phylogenomic, phenotypic, and biochemical analyses to determine the novel species statuses of both strains. The bacteria are available in BSRG-iBB’s culture collection associated with the ‘Portuguese Blue Biobank’ of the Blue Bioeconomy Pact and can be purchased at three internationally recognized culture collections - DSMZ, ATCC, and UCCCB.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...

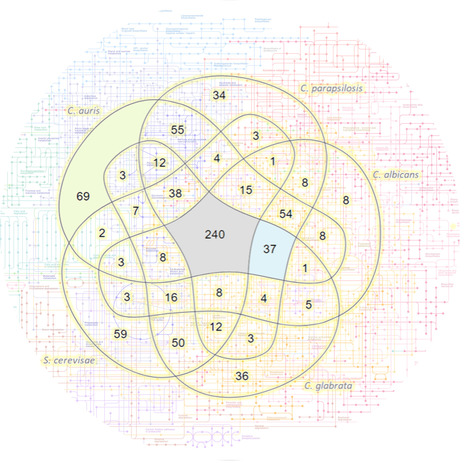
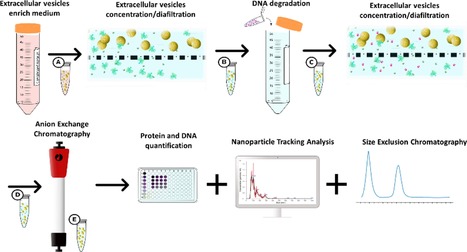

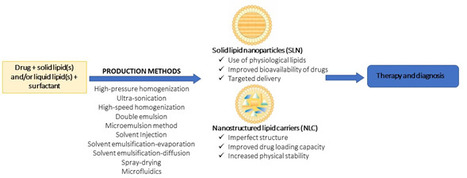





Check full paper here.