Despite very good safety records, clinical trials using plasmid DNA have failed due to low transfection efficiency and brief transgene expression. One of the reasons for this failure is poor plasmid design. In a paper published in Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering Reviews, researchers from iBB-BERG led by Gabriel Monteiro review critical aspects of plasmid design including promoter, polyadenylation signal, codon optimization and/or insertion of introns or nuclear-targeting sequences. The impact of detrimental elements like CpG motifs, selection markers, origins of replication, cryptic eukaryotic signals or nuclease-susceptible regions and inverted repeats is also examined. Click on title to learn more.
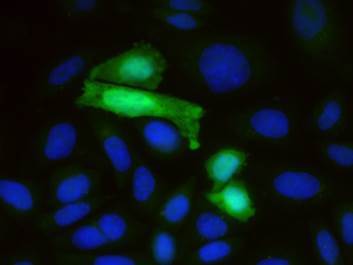
Photo details: CHO cells transfected with plasmid vector coding for GFP.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...