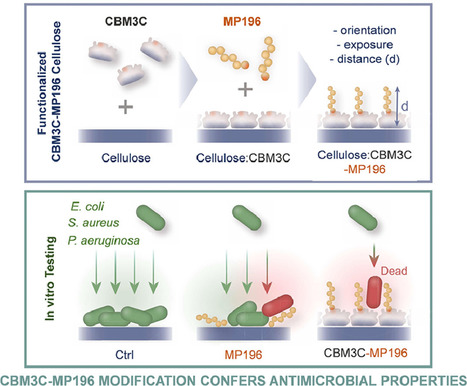
A new strategy to modify cellulose with the short antimicrobial hexapeptide MP196 (RWRWRW-NH2) is proposed by BERG and BSIRG researchers that uses fusions of Cys-terminated derivatives of MP196 and a carbohydrate binding module (CBM). CBM3-MP196-modified cellulose hydrogels displayed antibacterial activity that was significantly higher when compared with controls. This versatile concept offers a toolbox for the functionalization of different cellulose materials with a broad choice in peptides. the paper was published in Acta Biomaterialia. The work was funded by project CBM-X.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...