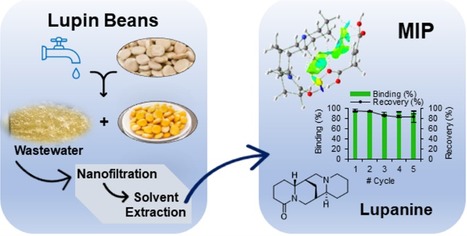
Lupanine is used as a building block in the synthesis of sparteine, a chiral selector in drug synthesis. This alkaloid is found in wastewaters derived from the debittering process that makes lupin beans edible. In a recently published work, carried out by researchers of the Faculty of Sciences and Faculty of Pharmacy from the University of Lisbon, and Teresa Esteves, Frederico Ferreira, Flávio Ferreira and Ana Mota from BERG-iBB, a computational chemistry approach was taken to design molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) selecting itaconic acid, a biobased building block, as a functional monomer that can provide higher affinities for lupanine. In this work, lupanine was concentrated from lupin bean wastewater by nanofiltration, extracted with ethyl acetate, and purified using the synthesized MIP, which was able to selectively recognize lupanine and improve its purity to 88%, with 82% recovery of the alkaloid, showing the potential application of this strategy to render the industrial process more sustainable.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...