 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
While the US debates the value of the modality, a South Korean survey finds that patients like to use audio-only telehealth platforms to connect with their care provider - but their providers aren’t so sure. While telehealth is not legally allowed in South Korea, the Ministry of Health and Welfare temporarily permitted its use due to hospital closures at the start of the pandemic. Between February 24 and March 7, 2020, 6,840 patients used audio-based telehealth. Researchers sent surveys to patients and providers alike to gauge their satisfaction with the telehealth platform, which includes landline telephones and online services without video. They asked questions about ease-of-use, interaction quality, reliability, satisfaction, and future use. Around 87 % of patients reported that they were satisfied with their provider interaction and felt they could effectively express their feelings during an audio-only telehealth visit. Most patients (87.1 %) also responded that their telehealth visit was just as reliable as an in-person visit would have been. Meanwhile, the providers’ opinions differed drastically. Less than 10 % of doctors and nurses were satisfied with their ability to interact with patients through an audio-only telehealth visit compared to in-person visits (7.3 % and 9 %, respectively). Only 14 % of providers felt that the visits were as reliable as an in-person visit. Patients and providers also had differing opinions on the convenience of telehealth. Nearly 80 % of patients were satisfied with the convenience of telehealth and found it easy to use. Providers were not as satisfied, with only 38.2 % of doctors and 30 percent of nurses reporting that they found telehealth convenient. Overall, providers felt the negatives outweighed the positives for audio-only telehealth. While 85.8 % of the doctors and nurses agreed that telehealth is appropriate for emergency situations such as a pandemic, only 27.7 said it would be appropriate at all times. In contrast, 40 % of the doctors and nurses surveyed said telehealth would be appropriate if it involved an audio-visual platform, saying it would be easier to fully examine and diagnose a patient’s condition. read more at https://mhealthintelligence.com/news/audio-only-telehealth-has-its-fans-patients-and-its-critics-providers

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
The COVID-19 pandemic is the greatest public health crisis of the last 100 years. Countries have responded with various levels of lockdown to save lives and stop health systems from being overwhelmed. At the same time, lockdowns entail large socioeconomic costs. One exit strategy under consideration is a mobile phone app that traces the close contacts of those infected with COVID-19. Recent research has demonstrated the theoretical effectiveness of this solution in different disease settings. However, concerns have been raised about such apps because of the potential privacy implications. This could limit the acceptability of app-based contact tracing in the general population. As the effectiveness of this approach increases strongly with app uptake, it is crucial to understand public support for this intervention. Objective: The objective of this study is to investigate the user acceptability of a contact-tracing app in five countries hit by the pandemic.
Methods: We conducted a largescale, multicountry study (N=5995) to measure public support for the digital contact tracing of COVID-19 infections.
We ran anonymous online surveys in France, Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, and the United States and measured intentions to use a contact-tracing app across different installation regimes (voluntary installation vs automatic installation by mobile phone providers) and studied how these intentions vary across individuals and countries.
Results: We found strong support for the app under both regimes, in all countries, across all subgroups of the population, and irrespective of regional-level COVID-19 mortality rates.
We investigated the main factors that may hinder or facilitate uptake and found that concerns about cybersecurity and privacy, together with a lack of trust in the government, are the main barriers to adoption.
Conclusions:
Epidemiological evidence shows that app-based contact tracing can suppress the spread of COVID-19 if a high enough proportion of the population uses the app and that it can still reduce the number of infections if uptake is moderate. Our findings show that the willingness to install the app is very high. The available evidence suggests that app-based contact tracing may be a viable approach to control the diffusion of COVID-19. read the study at https://mhealth.jmir.org/2020/8/e19857

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
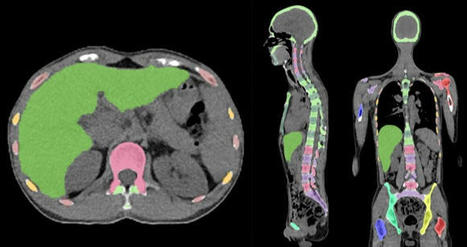
Skeleton/bone marrow involvement in patients with newly diagnosed Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) is an important predictor of adverse outcomes1. Studies show that FDG-PET/CT upstages patients with uni- or multifocal skeleton/bone marrow uptake (BMU) when iliac crest bone marrow biopsy fails to find evidence of histology-proven involvement. The general recommendation is, therefore, that bone marrow biopsy can be avoided when FDG-PET/CT is performed at staging. Our aim was to develop an AI-based method for the detection of focal skeleton/BMU and quantification of diffuse BMU in patients with HL undergoing staging with FDG-PET/CT. The output of the AI-based method in a separate test set was compared to the image interpretation of ten physicians from different hospitals. Finally, the AI-based quantification of diffuse BMU was compared to manual quantification. Artificial intelligence-based classification A convolutional neural network (CNN) was used to segment the skeletal anatomy11. Based on this CNN, the bone marrow was defined by excluding the edges from each individual bone; more precisely, 7 mm was excluded from the humeri and femora, 5 mm was excluded from the vertebrae and hip bones, and 3 mm was excluded from the remaining bones. Focal skeleton/bone marrow uptake The basic idea behind our approach is that the distribution of non-focal BMU has a light tail and most pixels will have an uptake reasonably close to the average. There will still be variations between different bones. Most importantly, we found that certain bones were much more likely to have diffuse BMU than others. Hence, we cannot use the same threshold for focal uptake in all bones. At the other end, treating each bone individually is too susceptible to noise. As a compromise, we chose to divide the bones into two groups: -
“spine”—defined as the vertebrae, sacrum, and coccyx as well as regions in the hip bones within 50 mm from these locations, i.e., including the sacroiliac joints. -
“other bones”—defined as the humeri, scapulae, clavicles, ribs, sternum, femora, and the remaining parts of the hip bones. For each group, the focal standardized uptake values (SUVs) were quantified using the following steps: - Threshold computation. A threshold (THR) was computed using the mean and standard deviation (SD) of the SUV inside the bone marrow. The threshold was set to
- 2. Abnormal bone region. The abnormal bone region was defined in the following way:
Only the pixels segmented as bone and where SUV > THR were considered. To reduce the issues of PET/CT misalignment and spill over, a watershed transform was used to assign each of these pixels to a local maximum in the PET image. If this maximum was outside the bone mask, the uptake was assumed to be leaking into the bone from other tissues and was removed. Finally, uptake regions smaller than 0.1 mL were removed. - 3.Abnormal bone SUV quantification. The mean squared abnormal uptake (MSAU) was first calculated as
MSAU=meanof(SUV−THR)2overtheabnormalboneregion. To quantify the abnormal uptake, we used the total squared abnormal uptake (TSAU), rather than the more common total lesion glycolysis (TLG). We believe TLG tends to overestimate the severity of larger regions with moderate uptake. TSAU will assign a much smaller value to such lesions, reflecting the uncertainty that is often associated with their classification. Instead, TSAU will give a larger weight to small lesions with very high uptake. This reflects both the higher certainty with respect to their classification and the severity typically associated to very high uptake. TSAU=MSAU×(volumeoftheabnormalboneregion). This calculation leads to two TSAU values; one for the “spine” and one for the “other bones”. As the TSAU value can be nonzero even for patients without focal uptake, cut-off values were tuned using the training cohort. The AI method was adjusted in the training group to have a positive predictive value of 65% and a negative predictive value of 98%. For the “spine”, a cut-off of 0.5 was used, and for the “other bones”, a cut-off of 3.0 was used. If one of the TSAU values was higher than the corresponding cut-off, the patient was considered to have focal uptake. Results Focal uptake Fourteen of the 48 cases were classified as having focal skeleton/BMU by the AI-based method. The majority of physicians classified 7/48 cases as positive and 41/48 cases as negative for having focal skeleton/BMU. The majority of the physicians agreed with the AI method in 39 of the 48 cases. Six of the seven positive cases (86%) identified by the majority of physicians were identified as positive by the AI method, while the seventh was classified as negative by the AI method and by three of the ten physicians. Thirty-three of the 41 negative cases (80%) identified by the majority of physicians were also classified as negative by the AI method. In seven of the remaining eight patients, 1–3 physicians (out of the ten total) classified the cases as having focal uptake, while in one of the eight cases none of the physicians classified it as having focal uptake. These findings indicate that the AI method has been developed towards high sensitivity, which is necessary to highlight suspicious uptake. Conclusions The present study demonstrates that an AI-based method can be developed to highlight suspicious focal skeleton/BMU in HL patients staged with FDG-PET/CT. This AI-based method can also objectively provide results regarding high versus low BMU by calculating the SUVmedian value in the whole spine marrow and the liver. Additionally, the study also demonstrated that inter-observer agreement regarding both focal and diffuse BMU is moderate among nuclear medicine physicians with varying levels of experience working at different hospitals. Finally, our results show that the automated method regarding diffuse BMU is comparable to the manual ROI method. read the original paper at https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-89656-9

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
As we move through the world, what we see is seamlessly integrated with our memory of the broader spatial environment. How does the brain accomplish this feat? A new study from Dartmouth College reveals that three regions of the brain in the posterior cerebral cortex, which the researchers call "place-memory areas," form a link between the brain's perceptual and memory systems. The findings are published in Nature Communications. For the study, an innovative methodology was employed. Participants were asked to perceive and recall places that they had been to in the real world during functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), which produced high-resolution, subject specific maps of brain activity. Past studies on scene perception and memory have often used stimuli that participants knew of but had never visited, like famous landmarks, and have pooled data across many subjects. By mapping the brain activity of individual participants using real-world places that they had been to, researchers were able to untangle the brain's fine-grained organization. In one experiment, 14 participants provided a list of people that they knew personally and places that they have visited in real-life (e.g., their father or their childhood home). Then, while in the fMRI scanner, the participants imagined that they were seeing those people or visiting those places. Comparing the brain activity between people and places revealed the place-memory areas. Importantly, when the researchers compared these newly identified regions to the brain areas that process visual scenes, the new regions were overlapping but distinct. "Learning how the mind is organized is at the heart of the quest of understanding what makes us human. The place-memory network provides a new framework for understanding the neural processes that drive memory-guided visual behaviors, including navigation," explains Robertson. The research team is currently using virtual reality technology to explore how representations in the place-memory areas evolve as people become more familiar with new environments. read the original unedited article at https://medicalxpress.com/news/2021-05-reveals-memories-familiar-brain.html read the study paper "A network linking scene perception and spatial memory systems in posterior cerebral cortex" at http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22848-z

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
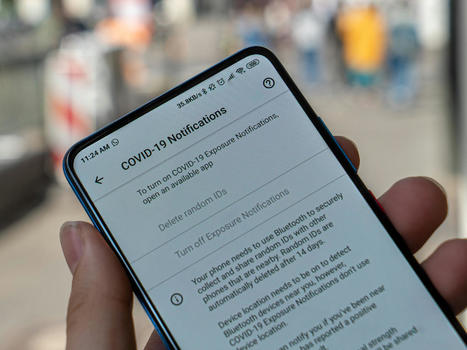
Contact tracing apps are potentially useful tools for supporting national COVID-19 containment strategies. Various national apps with different technical design features have been commissioned and issued by governments worldwide.
Objective: Our goal was to develop and propose an item set that was suitable for describing and monitoring nationally issued COVID-19 contact tracing apps.
This item set could provide a framework for describing the key technical features of such apps and monitoring their use based on widely available information.
Methods: We used an open-source intelligence approach (OSINT) to access a multitude of publicly available sources and collect data and information regarding the development and use of contact tracing apps in different countries over several months (from June 2020 to January 2021). The collected documents were then iteratively analyzed via content analysis methods. During this process, an initial set of subject areas were refined into categories for evaluation (ie, coherent topics), which were then examined for individual features.
These features were paraphrased as items in the form of questions and applied to information materials from a sample of countries (ie, Brazil, China, Finland, France, Germany, Italy, Singapore, South Korea, Spain, and the United Kingdom [England and Wales]). This sample was purposefully selected; our intention was to include the apps of different countries from around the world and to propose a valid item set that can be relatively easily applied by using an OSINT approach.
Results: Our OSINT approach and subsequent analysis of the collected documents resulted in the definition of the following five main categories and associated subcategories:
(1) background information (open-source code, public information, and collaborators); (2) purpose and workflow (secondary data use and warning process design); (3) technical information (protocol, tracing technology, exposure notification system, and interoperability); (4) privacy protection (the entity of trust and anonymity); and (5) availability and use (release date and the number of downloads). Based on this structure, a set of items that constituted the evaluation framework were specified. The application of these items to the 10 selected countries revealed differences, especially with regard to the centralization of the entity of trust and the overall transparency of the apps’ technical makeup.
Conclusions: We provide a set of criteria for monitoring and evaluating COVID-19 tracing apps that can be easily applied to publicly issued information. The application of these criteria might help governments to identify design features that promote the successful, widespread adoption of COVID-19 tracing apps among target populations and across national boundaries.
read the study at https://mhealth.jmir.org/2021/3/e27232

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
Patients with mental health conditions had positive perceptions about electronic medical records (EMRs) and physician clinical notes after being given full access to their records, according to a study published in the Annals of Family Medicine. Throughout the last 10 years, EMRs and clinical notes have become more accessible to patients, with some evidence suggesting the access helps patients become more engaged and confident with their doctors. Despite the benefits, some clinicians and doctors have concerns about sharing clinic notes with mental health patients due to safety reasons. In the study, a research team compared the perceptions patients with and without a mental health diagnosis had about EMRs after receiving full access to clinical notes through secure online portals. The team used data from an original OpenNotes study, which provided patients full access to their EMRs and clinical notes from multiple healthcare systems. The patients were then asked to complete a survey on their thoughts using EMRs. The survey was completed by 2,534 total patients—400 patients had a mental health diagnosis, while 2,134 patients did not. According to the results, patients with mental health conditions enjoyed having access to their records. “Compared with patients without mental health diagnoses, primary care patients with mental health diagnoses were similarly enthusiastic about the utility of reading their doctors’ notes online,” the study said.

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
The objective of this study was to investigate how users experience the implementation of self-regulation techniques
in a Web-based intervention targeting physical activity and sedentary behavior in the general population. Background: eHealth interventions show stronger effects when informed by solid behavioral change theories; for example,
self-regulation models supporting people in translating vague intentions to specific actions have shown to be effective in altering
health behaviors. Although these theories inform developers about which behavioral change techniques should be included, they
provide limited information about how these techniques can be engagingly implemented in Web-based interventions. Considering
the high levels of attrition in eHealth, investigating users’ experience about the implementation of behavior change techniques might be a fruitful avenue.
Results:
The techniques “providing feedback on performance,” “action planning,” and “prompting review of behavioral goals”
were appreciated by users. However, the implementation of “barrier identification/problem solving” appeared to frustrate users; this was also reflected by the users’ website data—many coping plans were of poor quality. Most users were well aware of the benefits of adopting a more active way of living and stated not to have learned novel information. However, they appreciated the provided information because it reminded them about the importance of having an active lifestyle. Furthermore, prompting users to self-monitor their behavioral change was not sufficiently stimulating to make users actually monitor their behavior. Conclusions: Iteratively involving potential end users offers guidance to optimally adapt the implementation of various
|

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
Adherence to treatment is critical for successful treatment outcomes. Although factors influencing antiretroviral therapy (ART) adherence vary, young adults are less likely to adhere owing to psychosocial issues such as stigma, ART-related side effects, and a lack of access to treatment. The Call for Life Uganda (CFLU) mobile health (mHealth) tool is a mobile phone–based technology that provides text messages or interactive voice response functionalities through a web interface and offers 4 modules of support.
Objective: This study aims to describe the acceptability and feasibility of a mobile phone support tool to promote adherence to ART among young adults in a randomized controlled trial.
Methods: An exploratory qualitative design with a phenomenological approach at 2 study sites was used. A total of 17 purposively selected young adults with HIV infection who had used the mHealth tool CFLU from 2 clinics were included. In total, 11 in-depth interviews and 1 focus group discussion were conducted to examine the following topics: experience with the CFLU tool (benefits and challenges), components of the tool, the efficiency of the system (level of comfort, ease, or difficulty in using the system), how CFLU resolved adherence challenges, and suggestions to improve CFLU. Participants belonged to 4 categories of interest: young adults on ART for the prevention of mother-to-child transmission, young adults switching to or on the second-line ART, positive partners in an HIV-discordant relationship, and young adults initiating the first-line ART. All young adults had 12 months of daily experience using the tool. Data were analyzed using NVivo version 11 software (QSR International Limited) based on a thematic approach.
Results: The CFLU mHealth tool was perceived as an acceptable intervention;
young adults reported improvement in medication adherence, strengthened clinician-patient relationships, and increased health knowledge from health tips. Appointment reminders and symptom reporting were singled out as beneficial and helped to address the problems of forgetfulness and stigma-related issues. HIV-related stigma was reported by a few young people. Participants requested extra support for scaling up CFLU to make it more youth friendly. Improving the tool to reduce technical issues, including network outages and a period of software failure, was suggested. They suggested that in addition to digital solutions, other support, including the promotion of peer support meetings and the establishment of a designated space and staff members for youth, was also important.
Conclusions: This mHealth tool was an acceptable and feasible strategy for improving ART adherence and retention among young adults in resource-limited settings.
read the entire study at https://mhealth.jmir.org/2021/6/e17418/

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
Identifying new COVID-19 cases is challenging. Not every suspected case undergoes testing, because testing kits and other equipment are limited in many parts of the world. Yet populations increasingly use the internet to manage both home and work life during the pandemic, giving researchers mediated connections to millions of people sheltering in place.
Objective: The goal of this study was to assess the feasibility of using an online news platform to recruit volunteers willing to report COVID-19–like symptoms and behaviors.
Methods: An online epidemiologic survey captured COVID-19–related symptoms and behaviors from individuals recruited through banner ads offered through Microsoft News. Respondents indicated whether they were experiencing symptoms, whether they received COVID-19 testing, and whether they traveled outside of their local area.
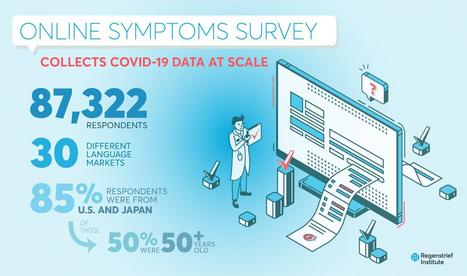
Results: A total of 87,322 respondents completed the survey across a 3-week span at the end of April 2020, with 54.3% of the responses from the United States and 32.0% from Japan. Of the total respondents, 19,631 (22.3%) reported at least one symptom associated with COVID-19. Nearly two-fifths of these respondents (39.1%) reported more than one COVID-19–like symptom. Individuals who reported being tested for COVID-19 were significantly more likely to report symptoms (47.7% vs 21.5%; P<.001). Symptom reporting rates positively correlated with per capita COVID-19 testing rates (R2=0.26; P<.001). Respondents were geographically diverse, with all states and most ZIP Codes represented. More than half of the respondents from both countries were older than 50 years of age.
Conclusions: News platforms can be used to quickly recruit study participants, enabling collection of infectious disease symptoms at scale and with populations that are older than those found through social media platforms. Such platforms could enable epidemiologists and researchers to quickly assess trends in emerging infections potentially before at-risk populations present to clinics and hospitals for testing and/or treatment.
source: Credit to Regenstrief Institute read the entire study here : https://www.jmir.org/2021/5/e24742

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
The aim of the Connected Healthcare Study was to understand the impact COVID-19 has had on health care and communication with providers and gain insights into experiences and preferences as it relates to telehealth and online health care tools. More than two-thirds of U.S. patients (69%) had seen a health care provider via telehealth since the COVID-19 pandemic began, with more than two in five (46%) meeting with a PCP and about one in five (19%) meeting with a mental health care provider. Other providers whom respondents have seen via telehealth since the pandemic began included specialties like ophthalmology and women’s health and orthopedic care, which were not considered typical telehealth users before the pandemic. Telehealth is clearly emerging from the COVID-19 pandemic as the new normal – an overwhelming majority (84%) of respondents who received telehealth services since March 2020 reported that they plan to continue using telehealth appointments in the future, with the top reasons being that it’s more convenient (43%) or to avoid being around people who are ill (39%). One of the most striking results of the survey was that nearly half of U.S. patients (48%) reported that they have sought (4%) or would be likely to seek care (44%) from a different health care provider if their current provider did not offer telehealth appointments. This is clearly a resounding message of support for telehealth from patients to their physicians. As we look back on the broader impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, it will have catapulted patient awareness and acceptance of telehealth and virtual care to the extent that would have been inconceivable before the pandemic. It has also brought to the forefront many other aspects of patient electronic and virtual engagement with providers across all specialties. read the entire post at https://www.kevinmd.com/blog/2021/05/how-do-patients-really-feel-about-virtual-care-and-electronic-patient-engagement.html

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
Mobile health apps are becoming increasingly popular, and they provide opportunities for effective health management. Existing chronic disease management (CDM) apps cannot meet users’ practical and urgent needs, and user adhesion is poor. Few studies, however, have investigated the factors that influence the continuance intention of CDM app users. Objective: Starting from the affordances of CDM apps, this study aimed to analyze how such apps can influence continuance intention through the role of health empowerment. Methods: Adopting a stimulus-organism-response framework, an antecedent model was established for continuance intention from the perspective of perceived affordances, uses and gratifications theory, and health empowerment. Perceived affordances were used as the “stimulus,” users’ gratifications and health empowerment were used as the “organism,” and continuance intention was used as the “response.” Data were collected online through a well-known questionnaire survey platform in China, and 323 valid questionnaires were obtained. The theoretical model was tested using structural equation modeling. Results: Perceived connection affordances were found to have significant positive effects on social interactivity gratification (t717=6.201, P<.001) and informativeness gratification (t717=5.068, P<.001). Perceived utilitarian affordances had significant positive effects - on informativeness gratification (t717=7.029, P<.001),
- technology gratification (t717=8.404, P<.001),
- and function gratification (t717=9.812, P<.001).
Perceived hedonic affordances had - significant positive effects on function gratification (t717=5.305, P<.001)
- and enjoyment gratification (t717=13.768, P<.001).
Five gratifications (t717=2.767, P=.005; t717=4.632, P<.001; t717=7.608, P<.001; t717=2.496, P=.012; t717=5.088, P<.001) had significant positive effects on health empowerment. Social interactivity gratification, informativeness gratification, and function gratification had significant positive effects on continuance intention. Technology gratification and enjoyment gratification did not have a significant effect on continuance intention. Health empowerment had a significant positive effect on continuance intention. Health empowerment and gratifications play mediating roles in the influence of affordances on continuance intention. Conclusions: Health empowerment and gratifications of users’ needs are effective ways to promote continuance intention. The gratifications of users’ needs can realize health empowerment and then inspire continuance intention. Affordances are key antecedents that affect gratifications of users’ needs, health empowerment, and continuance intention. The results indicated that users’ perceptions of an app’s affordances can promote the gratification of needs, and the gratification of key needs (ie, social interactivity, informativeness, technology, and function gratification) can stimulate users’ continuance intention. At the same time, the gratification of users’ needs can promote users’ cognitions of health empowerment, thus stimulating continuance intention. Health empowerment was found to play a mediating role in the influence of gratification on continuance intention. From a practical perspective, app service providers should design apps from the perspective of social interaction (eg, providing social networks), utilitarian functions (eg, health self-management), and hedonic functions (eg, enhancing the user’s interest). By meeting users’ various needs, app developers can improve the user’s ability to control his or her own health, thus achieving the purpose of extending the life of the app. more at https://mhealth.jmir.org/2021/5/e21831/

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
Many viruses infect their hosts through mucosal surfaces such as the lining of the respiratory tract. MIT researchers have now developed a vaccination strategy that can create an army of T cells that are ready and waiting at those surfaces, offering a quicker response to viral invaders. The researchers showed that they could induce a strong memory T cell response in the lungs of mice by giving them a vaccine modified to bind to a protein naturally present in mucus. This can help ferry the vaccine across mucosal barriers, such as the lining of the lungs “In this paper, we specifically focused on T cell responses that would be useful against viruses or cancer, and our idea was to use this protein, albumin, as sort of a Trojan horse to get the vaccine across the mucosal barrier,” says Darrell Irvine, the senior author of the study, who is the Underwood-Prescott Professor with appointments in the departments of Biological Engineering and Materials Science and Engineering; an associate director of MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research; and a member of the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT, and Harvard. In addition to protecting against pathogens that infect the lungs, these types of inhaled vaccines could also be used to treat cancer metastasizing to the lungs or even prevent cancer from developing in the first place, the researchers say. read the release from the MIT news Office at https://news.mit.edu/2021/vaccination-inhalation-0319

|
Scooped by
nrip
|
The Purpose of this study was to synthesize evidence of the effects and potential effect modifiers of different electronic health (eHealth) interventions to help people quit smoking. Four databases (MEDLINE, PsycINFO, Embase, and The Cochrane Library) were searched in March 2017 using terms that included “smoking cessation”, “eHealth/mHealth” and “electronic technology” to find relevant studies. Meta-analysis and meta-regression analyses were performed.
Results: The review included 108 studies and 110,372 participants. Compared to nonactive control groups (eg, usual care), smoking cessation interventions using web-based and mobile health (mHealth) platform resulted in significantly greater smoking abstinence.
Similarly, smoking cessation trials using tailored text messages and web-based information and conjunctive nicotine replacement therapy may also increase cessation. In contrast, little or no benefit for smoking abstinence was found for computer-assisted interventions. The magnitude of effect sizes from mHealth smoking cessation interventions was likely to be greater if the trial was conducted in the USA or Europe and when the intervention included individually tailored text messages. In contrast, high frequency of texts (daily) was less effective than weekly texts. Conclusion There was consistent evidence that web-based and mHealth smoking cessation interventions may increase abstinence moderately. Methodologic quality of trials and the intervention characteristics (tailored vs untailored) are critical effect modifiers among eHealth smoking cessation interventions, especially for web-based and text messaging trials. Future smoking cessation intervention should take advantages of web-based and mHealth engagement to improve prolonged abstinence. access the study report at https://www.dovepress.com/which-ehealth-interventions-are-most-effective-for-smoking-cessation-a-peer-reviewed-article-PPA
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
















The idea of being able to literally have a check-up has jumped to the forefront in terms of convenience. While some believe Audio-only is a level of impersonal (providers), most whom needed to use the service (patients) believed it was very effect in terms of being diagnosed. Practitioners of the medical arts feel that this innovative idea can be expanded for a more accurate interaction with patients by also integrating visual/video with this program. With the rapid expansion of tech, it may not be long before you only need to actually go to the hospital when in need of critical care. This would lead to hospitals being able to take in more patients that actually need to be there vs ones taking up space because of the "convenience" of being closer physically. The one drawback I foresee may be the fact of availability of your actual doctor, though it could be be supplemented by other professionals in the field.