Algorithms based on machine learning and deep learning, intended for use in diagnostic imaging, are moving into the commercial pipeline.
However, providers will have to overcome multiple challenges to incorporate these tools into daily clinical workflows in radiology.
There now are numerous algorithms in various stages of development and in the FDA approval process, and experts believe that there could eventually be hundreds or even thousands of AI-based apps to improve the quality and efficiency of radiology.
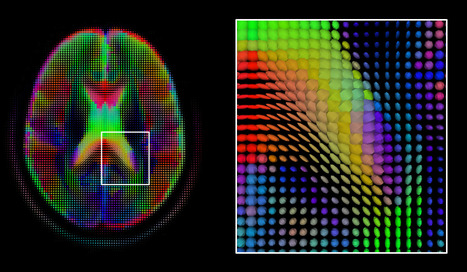
The emerging applications based on machine learning and deep learning primarily involve algorithms to automate such processes in radiology as detecting abnormal structures in images, such as cancerous lesions and nodules. The technology can be used on a variety of modalities, such as CT scans and X-rays. The goal is to help radiologists more effectively detect and track the progression of diseases, giving them tools to enhance speed and accuracy, thus improving quality and reducing costs.
While the number of organizations incorporating these products into daily workflows is small today, experts expect many providers to adopt these solutions as the industry overcomes implementation challenges.
Data dump
Radiologists’ growing appreciation for AI may result from the technology’s promise to help the profession cope with an explosion in the amount of data for each patient case.
Radiologists also are grappling with the growth in data from sources outside radiology, such as lab tests or electronic medical records. This is another area where AI could help radiologists by analyzing data from disparate sources and pulling out key pieces of information for each case,.
There are other issues that AI could address as well, such as “observer fatigue,” which is an “aspect of radiology practice and a particular issue in screening examinations where the likelihood of finding a true positive is low,” wrote researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in a 2018 article in the Journal of the American College of Radiology.
These researchers foresee the utility of an AI program that could identify cases from routine screening exams with a likely positive result and prioritize those cases for radiologists’ attention.
AI software also could help radiologists improve worklists of cases in which referring physicians already suspect that a medical problem exists.
read more at the original source: https://www.healthdatamanagement.com/news/algorithms-begin-to-show-practical-use-in-diagnostic-imaging



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...