 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 24, 2020 8:32 AM
|
Pendant une longue période, les réseaux Ethernet de datacenter ont été bâtis en strates selon des architectures rappelant un arbre hiérarchique. Ce système hiérarchique est en train de trouver ses limites avec l’explosion des trafics de données entre serveurs (trafic dit Est- Ouest, par opposition au trafic Nord-Sud, qui va des serveurs vers les utilisateurs).

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 23, 2020 8:40 AM
|
Toute infrastructure hébergeant plusieurs projets ou clients nécessite une isolation réseau réelle. Avant la démocratisation des outils, fournisseurs et méthodes liées au cloud, la méthode couramment utilisée pour proposer cette isolation en datacenter était l’utilisation des VLANs (norme 802.1Q) qui étaient configurés directement sur les équipements réseau de

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 23, 2020 8:33 AM
|
"Internet traffic is expected to grow at 30% year-over-year, give or take," is a well-known truism in the industry. Every five years internet traffic i

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 8, 2020 4:46 AM
|
Difference Between Overlay And Underlay Network In Tabular Form BASIS OF COMPARISON UNDERLAY NETWORK OVERLAY NETWORK Description Underlay Network is physical infrastructure above which overlay network is built. An Overlay Network is a virtual network that is built on top of an underlying Network infrastructure/Network layer (the underlay). Traffic Flow Transmits packets which traverse over network devices like switches and routers. Transmits packets only along the virtual links between the overlay nodes. Deployment Time Less scalable and time consuming activity to setup new services and functions. Ability to rapidly and incrementally deploy new functions through edge-centric innovations. Packet Control Hardware oriented. Software oriented. Packet Encapsulation And Overhead Packet delivery and reliability occurs at layer-3 and layer-4. Needs to encapsulate packets across source and destination, hence incurs additional overhead. Multipath Forwarding Less scalable options of multipath forwarding. In fact using multiple paths can have associated overhead and complexity. Support for multi-path forwarding within virtual networks. Managing Multitenancy NAT or VRF based segregation required which may face challenge in big environments. Ability to manage overlapping IP addresses between multiple tenants. Scalability Less Scalable due to technology limitation. Designed to provide more scalability than underlay network. E.g VLAN (Underlay Network) provides 4096 VLAN support while VXLAN (Overlay Network) provides up to 16 million identifiers. Packet Delivery Responsible for delivery of packets. Offloaded from delivery of packets. Protocols Underlay protocols include Ethernet Switching, VLAN, Routing etc. Overlay network protocols include Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN), Network Virtualization using Generic Encapsulation (NVGRE), Stateless Transport Tunning (SST), Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE), IP multicast and Network Virtualization overlays 3 (NVO3).

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 8, 2020 4:45 AM
|
Depuis plusieurs années, le SDN est un terme à la mode. Parfois galvaudé, il est plus délicat à appréhender qu’il n’y parait. Si l’on peut le qualifier de disruptif dans le domaine des réseaux, il convient toutefois de bien en comprendre les apports mais aussi les limites.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
October 30, 2019 10:46 AM
|
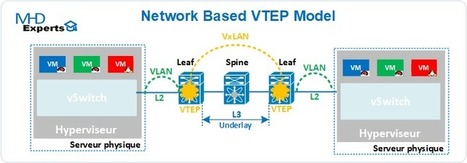
Dans un précédent article nous avons présenté VLXAN. STT, NVGRE et GENEVE sont d’autres exemples de protocoles d’encapsulation qui permettent de construire un overlay (à la manière d’IPSEC dans certains déploiements de Kubernetes sur un Cloud public) pour des réseaux de type SDN. Un point d’attention particulier est la façon dont les points de terminaison (VTEP : VXLAN Tunnel EndPoint) découvrent leurs pairs et renseignent la table de correspondance (ou mapping) @MAC <=> VTEP.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 19, 2019 3:47 AM
|
The phrase was first coined in 1984 by John Gage, the 21st employee of Sun Microsystems, where he was credited with building Sun’s vision around “The Network is the Computer.”

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 17, 2019 10:49 AM
|
We shared with everyone the ONF’s new Strategic Plan back in March, and since then our community has been hard at work kicking off all the new initiatives called for in the plan. Our operator leadership has been making great progress, and we want to take a moment to summarize where we are and how …

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 17, 2019 10:46 AM
|
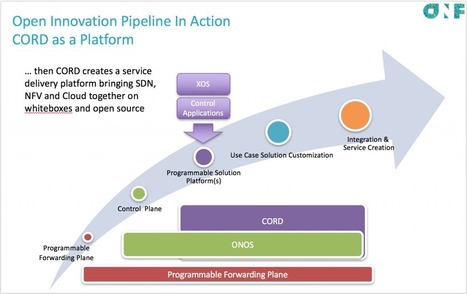
The ONF has announced an initiative to integrate white box switches, open source networking software & SDN to help telcos re-architect their infrastructure

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 9, 2019 12:47 PM
|
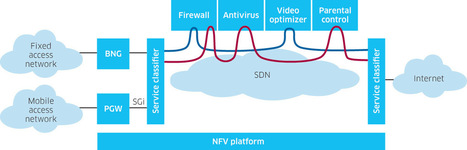
Network service chaining and service function chaining use SDN capabilities for service chain provisioning to connect virtualized network services.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 9, 2019 4:47 AM
|
SDN and NFV enable software-driven service chain provisioning, making it easier and cheaper to spin up applications in enterprise and service provider networks.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 9, 2019 4:22 AM
|
The rise of SDN has led to increased discussion of service chaining, but many don't fully grasp its use or its potential benefits.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 5, 2019 3:57 AM
|
Le protocole standard Netconf (normalisé dans le RFC 6241) permet de configurer un équipement réseau (par exemple un commutateur) à distance. Netconf fonctionne par des RPC dont les paramètres sont des actions à faire effectuer par l'équipement configuré, ou bien les nouvelles valeurs que peut prendre telle ou telle des variables de configuration de cet équipement. Mais comment savoir quelles actions sont possibles, quelles variables existent, et quelles valeurs elles peuvent prendre ? Jusqu'à présent, cela pouvait se spécifier uniquement dans une documentation en langue naturelle fournie avec l'équipement. Désormais, il est possible de spécifier ces informations dans un langage formel, Yang, que décrit notre RFC. Ce RFC 6020 est très détaillé, près de deux cents pages. Et je n'ai pas personnellement d'expérience pratique avec Yang. Donc, je ne donne ici qu'un très bref résumé. Un tel survol se trouve également dans la section 4 du RFC : Yang modélise les données qui seront utilisées par Netconf. Ces données sont représentées sous forme arborescente. Yang est modulaire (section 5 du RFC), un module Yang pouvant se référer à d'autres modules. Yang définit un ensemble de types pour décrire les données (section 9 et RFC 6991). Il permet également d'indiquer les contraintes que doivent respecter les données. Yang, langage de haut niveau, ne décrit pas l'encodage utilisé sur le câble. Yang a donc bien des points communs avec le SMI des RFC 2578 et RFC 2579. Avant Netconf, beaucoup de gens pensaient que toute la gestion des équipements réseau se ferait en SNMP, en s'appuyant sur ce modèle SMI. Si, pour la lecture des variables, SNMP s'est largement imposé, force est de constater que, pour l'écriture de variables et pour les actions, SNMP reste très peu utilisé, au profit de toute une galaxie de mécanismes privés (Web, REST, SSH + CLI, etc), galaxie que Netconf vise à remplacer. Une MIB du SMI peut donc être traduite en Yang, l'inverse n'étant pas vrai (Yang étant plus riche).
|

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 23, 2020 8:42 AM
|
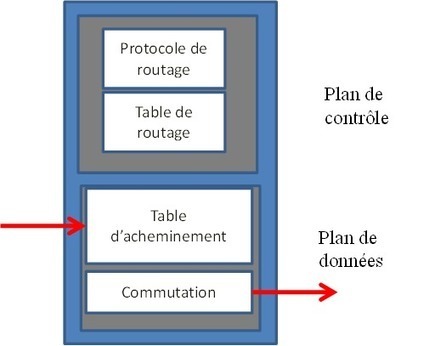
Le SDN (Software Defined Network) est le sujet d’actualité du moment, sa déclinaison pour les réseaux en Datacenter porte le nom de SDDC (Software Defined Data Center) dont le concept consiste à virtualiser tous les composants de l’infrastructure DC (Réseau, Stockage, Compute, Sécurité) et de les délivrer comme des services, l’objectif final recherché est un gain en agilité.
Pour permettre cette virtualisation sur le domaine réseau, il faut d’abords réduire la complexité par à une abstraction de la couche réseau des services qu’elle porte par l’implémentation de :
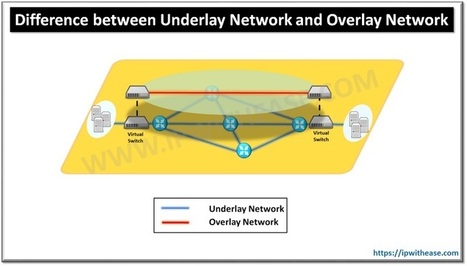
Une couche Underlay composée de commutateurs et de routeurs interconnectés ensemble pour transporter les paquets entre deux points du réseau : les décisions de commutation et de routage sont effectués par le calcul du « next-hop » en utilisant les protocoles L2/L3 traditionnels (OSPF, IS-IS, etc.)
Une couche Overlay qui désigne le réseau virtuel implémenté sur l’infrastructure physique et qui permet d’apporter une abstraction des décisions de routage et de filtrage pour être au plus proche des applications et des services.
Dans cet article, nous allons nous intéresser de près à la couche Overlay qui crée beaucoup de confusions et de comparaisons (parfois inutiles) entre les constructeurs et éditeurs de solutions, le but recherché est de lister les avantages et inconvénients de chaque solution et d’identifier les impacts en terme d’architecture réseau et son évolutivité, performances, implémentation de la solution, gestes d’exploitation et de résolution d’incidents.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 23, 2020 8:37 AM
|
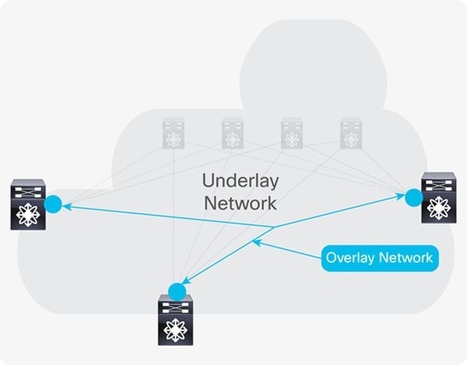
Network Overlays –
Network overlays is the latest solution to meet these demands, in fact, this technology can speed configuration of new or existing services.
Underlay Network –
Underlay Network is different from Underlay Network which IT industry has known for years. Underlay Network is physical infrastructure above which overlay network is built. It is the underlying network responsible for delivery of packets across networks.
Overlay Network –
An Overlay Network is a virtual network that is built on top of underlying network infrastructure (Underlay Network). Actually, “Underlay” provides a “service” to the overlay

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 23, 2020 8:32 AM
|
Cisco FabricPath, VXLAN flood-and-learn, VXLAN MP-BGP EVPN, and MSDC Layer 3 spine-and-leaf networks address fabric requirements in modern virtualized data centers.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 8, 2020 4:46 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 8, 2020 4:45 AM
|
Overlay technologies such as VXLAN have redefined the way data centers are operated. But how aware is the overlay about the physical network underneath.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
October 1, 2019 4:25 AM
|
Software Defined Networking - A way to controlling the network from a logically centralized high level program i.e. Controller.
- Decouples control plane from data plane.
- Network Virtualization is one of the application of SDN – Software defined networking can be leveraged as a tool to achieve Network Virtualization.
Network Virtualization - Carving out multiple virtual network from a single physical network
- Administration of each virtual network is delegated to same or different entity
- Administrator of one virtual network doesn’t have access to the traffic flowing through other virtual networks even if they are sharing the same physical link
- Virtualization can happen at many levels/layers e.g. at Routers (L3), Ethernet (L2), OTN (L1) or Wavelength (L0)
- Better utilization of network resources

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 17, 2019 10:50 AM
|
L'association ONF, compte dans ses rangs une douzaine de nouveaux membres, dont Alcatel-Lucent, Colt ou encore France Telecom.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 17, 2019 10:48 AM
|
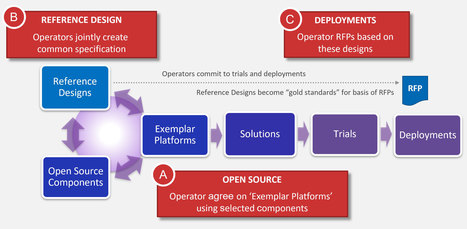
Reference Designs Reference Designs (RDs) represent a particular assembly of components that are required to build a deployable platform. They are “blueprints” developed by ONF’s Operator members to address specific use cases for the emerging edge cloud. ONF’s operator leadership expanded ONF’s mission to create a new strategic plan to deploy open source solutions into their …

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 17, 2019 10:45 AM
|
The Open Networking Foundation, a user-led organization, focuses on the adoption of open standards and SDN such as OpenFlow.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 9, 2019 11:45 AM
|
Service chaining has been getting a lot of press — and I’m encountering it a lot in the customers I’m talking to. What’s the big deal? To understand service chaining, let’s look at a really simple example, illustrated below (as always, you can click on the image to get a bigger version).

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 9, 2019 4:31 AM
|
IEEE SDN is a broad-based collaborative project focused on Software Defined Networks and Network Function Virtualization (NFV). Join our community to get involved in conferences, standards, educational opportunities, publications, and latest innovations in the areas of SDN and NFV.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 5, 2019 3:58 AM
|
Deux grandes familles de protocole sont définies : Le protocole interne domaine (OSPF, RIP, MPLS) et le protocole d’interconnexion inter domaine (BGP, EGP – Exterieur Gateway Protocol, …).
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...




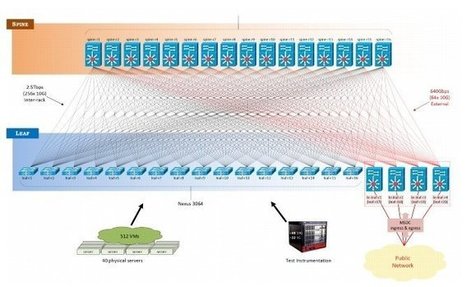


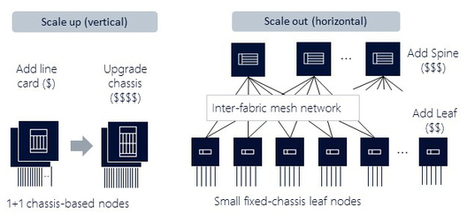

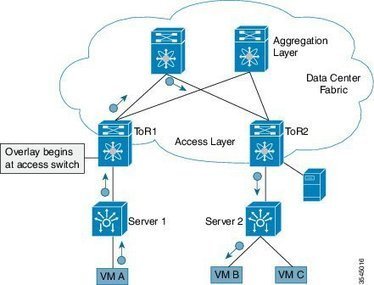








Dans les datacenters plus récents, on a donc vu émerger une alternative à l’architecture hiérarchique traditionnelle, connue sous le nom de Leaf-Spine (littéralement, feuille-épine dorsale). Dans ce modèle, une série de commutateurs, généralement positionnés en haut de rack, constituent la couche d’accès. Ces commutateurs disposent de liens complètement maillés avec des commutateurs de plus haut niveau qui constituent l’épine dorsale du réseau de datacenter.
Ce maillage permet de garantir qu’aucun nœud du réseau n’est à plus d’un bond (« hop ») » réseau d’un autre, ce qui permet entre autres de minimiser la latence, et l’apparition de goulets d’étranglement entre commutateurs d’accès. Lorsque les constructeurs parlent d’une « fabric » Ethernet, c’est en général à ce genre de topologie qu’ils pensent.