Background
We performed a systematic review to assess whether we can quantify the underreporting of adverse events (AEs) in the published medical literature documenting the results of clinical trials as compared with other nonpublished sources, and whether we can measure the impact this underreporting has on systematic reviews of adverse events.
Methods and Findings
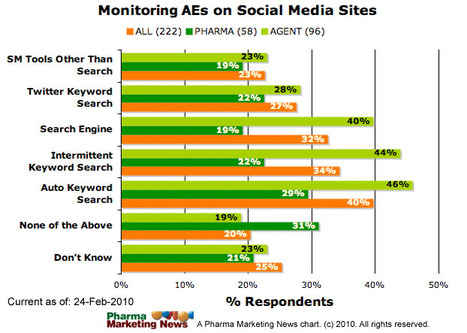
Studies were identified from 15 databases (including MEDLINE and Embase) and by handsearching, reference checking, internet searches, and contacting experts. The last database searches were conducted in July 2016. There were 28 methodological evaluations that met the inclusion criteria. Of these, 9 studies compared the proportion of trials reporting adverse events by publication status.
The median percentage of published documents with adverse events information was 46% compared to 95% in the corresponding unpublished documents. There was a similar pattern with unmatched studies, for which 43% of published studies contained adverse events information compared to 83% of unpublished studies.
A total of 11 studies compared the numbers of adverse events in matched published and unpublished documents. The percentage of adverse events that would have been missed had each analysis relied only on the published versions varied between 43% and 100%, with a median of 64%. Within these 11 studies, 24 comparisons of named adverse events such as death, suicide, or respiratory adverse events were undertaken. In 18 of the 24 comparisons, the number of named adverse events was higher in unpublished than published documents. Additionally, 2 other studies demonstrated that there are substantially more types of adverse events reported in matched unpublished than published documents. There were 20 meta-analyses that reported the odds ratios (ORs) and/or risk ratios (RRs) for adverse events with and without unpublished data. Inclusion of unpublished data increased the precision of the pooled estimates (narrower 95% confidence intervals) in 15 of the 20 pooled analyses, but did not markedly change the direction or statistical significance of the risk in most cases.
The main limitations of this review are that the included case examples represent only a small number amongst thousands of meta-analyses of harms and that the included studies may suffer from publication bias, whereby substantial differences between published and unpublished data are more likely to be published.
Conclusions
There is strong evidence that much of the information on adverse events remains unpublished and that the number and range of adverse events is higher in unpublished than in published versions of the same study. The inclusion of unpublished data can also reduce the imprecision of pooled effect estimates during meta-analysis of adverse events.
Via Pharma Guy

 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...