Your new post is loading...
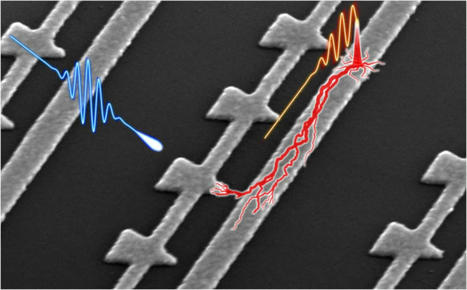
MIT researchers develop compact on-chip device for detecting electric-field waveforms with attosecond time resolution. Understanding how light waves oscillate in time as they interact with materials is essential to understanding light-driven energy transfer in materials, such as solar cells or plants. Due to the fantastically high speeds at which light waves oscillate, however, scientists have yet to develop a compact device with enough time resolution to directly capture them. Now, a team led by MIT researchers has demonstrated chip-scale devices that can directly trace the weak electric field of light waves as they change in time. Their device, which incorporates a microchip that uses short laser pulses and nanoscale antennas, is easy to use, requiring no special environment for operation, minimal laser parameters, and conventional laboratory electronics. The team’s work, published earlier this month in Nature Photonics, may enable the development of new tools for optical measurements with applications in areas such as biology, medicine, food safety, gas sensing, and drug discovery. “The potential applications of this technology are many,” says co-author Phillip Donnie Keathley, group leader and Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE) research scientist. “For instance, using these optical sampling devices, researchers will be able to better understand optical absorption pathways in plants and photovoltaics, or to better identify molecular signatures in complex biological systems.”
Via Tony Shan
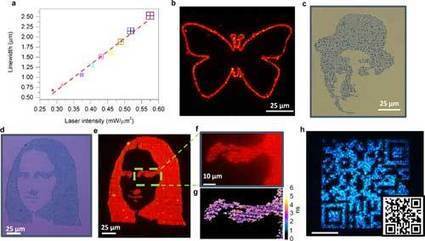
The use of quantum dots (QDs) in practical applications relies on the ability to precisely pattern QDs on substrates with desired optical properties. Typical direct-write printing techniques such as inkjet and gravure printing are limited in resolution (micron-scale), structural complexity, and require significant post-processing time.In new work, researchers at the University of Texas at Austin use laser-induced bubble printing to pattern CdSe/CdS QDs on plasmonic substrates with submicron resolution (<700nm line width), high throughput (∼10E4 µm/s) and strong QD-substrate adhesion.Not only is the bubble-mediated immobilization at the submicron scale stable, but the submicron-sized bubble's stability can be maintained over a large area. This technique is also compatible with flexible substrates and can be further integrated with smartphone to realize haptic integration. Finally, the emission characteristics of the QDs in terms of the emission wavelength and lifetime can be modified in real-time to achieve site-sensitive emission.The team, led by Yuebing Zheng, Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science & Engineering has been published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces ("High-Resolution Bubble Printing of Quantum Dots").
A team of UTS researchers has made a major breakthrough that could pave the way for the next generation of quantum communications.
The team, from the Materials and Technology for Energy Efficiency Research Strength at UTS Science, has found a material that emits a single pulse of a quantum light on demand at room temperature, removing one of the barriers to extremely fast and secure information processing.
Until now, room-temperature quantum emitters have only been observed in three-dimensional materials such as diamonds that hinder integration of these components in chips and commercial devices. The world is therefore in a race to find quantum light sources in atomically thin materials such as graphene – the famous single layer of carbon atoms.
"This material – layered hexagonal boron nitride (boron and nitrogen atoms that are arranged in a honeycomb structure) – is rather unique," Associate Professor Mike Ford said. "It is atomically thin and is traditionally used as a lubricant; however upon careful processing it can emit quantised pulses of light – single photons that can carry information.
"That's important because one of the big goals is to make optical computer chips that can operate based on light rather than electrons, therefore operating much faster with less heat generation."
The single photon sources were discovered by Trong Toan Tran, Kerem Bray, Mike Ford, Milos Toth and Igor Aharonovich from UTS Science, whose findings have just been published in the prestigious journal Nature Nanotechnology.
PhD candidate Trong Toan Tran said the results demonstrate the unprecedented potential of hexagonal boron nitride for large-scale nanophotonics and quantum information processing devices.
"This material is very easy to fabricate," he said. "It's a much more viable option because it can be used at room temperature; it's cheap, sustainable and is available in large quantities.
"Ultimately we want to build a 'plug and play' device that can generate single photons on demand, which will be used as a first prototype source for scalable quantum technologies that will pave the way to quantum computing with hexagonal boron nitride," he said.
The secret of X-ray science – like so much else – is in the timing. Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have created a new way of manipulating high-intensity X-rays, which will allow researchers to select extremely brief but precise X-ray bursts for their experiments.
The new technology, developed by a team of scientists from Argonne’s Center for Nanoscale Materials (CNM) and the Advanced Photon Source (APS), involves a small microelectromechanical system (MEMS) mirror only as wide as a few hairs.
MEMS are microscale devices fabricated using silicon wafers in facilities that make integrated circuits. The MEMS device acts as an ultrafast mirror reflecting X-rays at precise times and specific angles.
“Extremely compact devices such as this promise a revolution in our ability to manipulate photons coming from synchrotron light sources, not only providing an on-off switch enabling ultrahigh time-resolution studies, but ultimately promising new ways to steer, filter, and shape X-ray pulses as well,” said Stephen Streiffer, Associate Laboratory Director for Photon Sciences and Director of the Advanced Photon Source. “This is a premier example of the innovation that results from collaboration between nanoscientists and X-ray scientists.”
The device that the Argonne researchers developed essentially consists of a tiny diffracting mirror that oscillates at high speeds. As the mirror tilts rapidly back and forth, it creates an optical filter that selects only the X-ray pulses desired for the experiment. Only the light that is diffracted from the mirror goes on to hit the sample, and by adjusting the speed at which the MEMS mirror oscillates, researchers can control the timing of the X-ray pulses.
According to Argonne nanoscientist Daniel Lopez, one of the lead authors on the paper, the device works because of the relationship between the frequency of the mirror’s oscillation and the timing of the positioning of the perfect angle for the incoming X-ray. “If you sit on a Ferris wheel holding a mirror, you will see flashes of light every time the wheel is at the perfect spot for sunlight to hit it. The speed of the Ferris wheel determines the frequency of the flashes you see,” he said.
“The Argonne team’s work is incredibly exciting because it creates a new class of devices for controlling X-rays,” added Paul Evans, a professor of materials science at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. “They have found a way to significantly shrink the optics, which is great because smaller means faster, cheaper to make, and much more versatile.”
The ultimate challenge in the race to miniaturize light emitting diodes (LED) has now been met: a team led by the Institut de Physique et de Chimie des Matériaux de Strasbourg has developed the first ever single-molecule LED.
The device is formed from a single polythiophene wire placed between the tip of a scanning tunneling microscope and a gold surface. It emits light only when the current passes in a certain direction. This experimental tour de force sheds light on the interactions between electrons and photons at the smallest scales. Moreover, it represents yet another step towards creating components for a molecular computer in the future. This work has recently been published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Light emitting diodes are components that emit light when an electric current passes through them and only let light through in one direction. LEDs play an important role in everyday life, as light indicators. They also have a promising future in the field of lighting, where they are progressively taking over the market. A major advantage of LEDs is that it is possible to make them very small, so point light sources can be obtained. With this in mind, one final miniaturization hurdle has recently been overcome.
To achieve this, they used a single polythiophene wire. This substance is a good electricity conductor. It is made of hydrogen, carbon and sulfur, and is used to make larger LEDs that are already on the market. The polythiophene wire was attached at one end to the tip of a scanning tunneling microscope, and at the other end to a gold surface. The scientists recorded the light emitted when a current passed through this nanowire. They observed that the thiophene wire acts as a light emitting diode: light was only emitted when electrons went from the tip of the microscope towards the gold surface.. When the polarity was reversed, light emission was negligible.
In collaboration with a theoretical team from the Service de Physique de l'Etat Condensé, the researchers showed that this light was emitted when a negative charge (an electron) combined with a positive charge (a hole) in the nanowire and transmitted most of its energy to a photon. For every 100,000 electrons injected into the thiophene wire, a photon was emitted. Its wavelength was in the red range.
Graphene-based supercapacitors have already proven the equal of conventional supercapacitors – in the lab. But now researchers at Melbourne’s Monash University claim to have developed of a new scalable and cost-effective technique to engineer graphene-based supercapacitors that brings them a step closer to commercial development. With their almost indefinite lifespan and ability to recharge in seconds, supercapacitors have tremendous energy-storage potential for everything from portable electronics, to electric vehicles and even large-scale renewable energy plants. But the drawback of existing supercapacitors has been their low energy density of around 5 to 8 Wh/liter, which means they either have to be exceedingly large or recharged frequently. Professor Dan Li and his team at Monash University’s Department of Materials Engineering has created a graphene-based supercapacitor with an energy density of 60 Wh/liter, which is around 12 times higher than that of commercially available supercapacitors and in the same league as lead-acid batteries. The device also lasts as long as a conventional battery. To maximize the energy density, the team created a compact electrode from an adaptive graphene gel film they had previously developed. To control the spacing between graphene sheets on the sub-nanometer scale, the team used liquid electrolytes, which are generally used as the conductor in conventional supercapacitors. Unlike conventional supercapacitors that are generally made of highly porous carbon with unnecessarily large pores and rely on a liquid electrolyte to transport the electrical charge, the liquid electrolyte in Li’s team’s supercapacitor plays a dual role of conducting electricity and also maintaining the minute space between the graphene sheets. This maximizes the density without compromising the supercapcitor’s porosity, they claim. To create their compact electrode, the researchers used a technique similar to one used in traditional paper making, which they say makes the process cost-effective and easily scalable for industrial applications. "We have created a macroscopic graphene material that is a step beyond what has been achieved previously. It is almost at the stage of moving from the lab to commercial development," Professor Li said.
Researchers from the University of Bordeaux in Franceused high-frequency sound waves to test the stiffness and viscosity of the nuclei of individual human cells to help answer questions such as how cells adhere to medical implants and why healthy cells turn cancerous. “We have developed a new non-contact, non-invasive tool to measure the mechanical properties of cells at the sub-cell scale,” says Bertrand Audoin, a professor in the mechanics laboratory at the University of Bordeaux. “This can be useful to follow cell activity or identify cell disease.” The technique, called picosecond ultrasonics, was initially developed to measure the thickness of semiconductor chip layers. The researchers grew cells on a metal plate and then flashed the cell-metal interface with an ultra-short laser pulse to generate high-frequency sound waves. Another laser measured how the sound pulse propagated through the cells, giving the scientists clues about the mechanical properties of the individual cell components. “The higher the frequency of sound you create, the smaller the wavelength, which means the smaller the objects you can probe” says Audoin. “We use gigahertz waves, so we can probe objects on the order of a hundred nanometers.” For comparison, a cell’s nucleus is about 10,000 nanometers wide. In the coming years, the team envisions studying cancer cells with sound. “A cancerous tissue is stiffer than a healthy tissue,” notes Audoin. “If you can measure the rigidity of the cells while you provide different drugs, you can test if you are able to stop the cancer at the cell scale.”
As technology advances, it tends to shrink. From cell phones to laptops—powered by increasingly faster and tinier processors—everything is getting thinner and sleeker. And now light beams are getting smaller, too.
Engineers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) have created a device that can focus light into a point just a few nanometers (billionths of a meter) across—an achievement they say may lead to next-generation applications in computing, communications, and imaging. Because light can carry greater amounts of data more efficiently than electrical signals traveling through copper wires, today's technology is increasingly based on optics. The world is already connected by thousands of miles of optical-fiber cables that deliver email, images, and the latest video gone viral to your laptop. As we all produce and consume more data, computers and communication networks must be able to handle the deluge of information. Focusing light into tinier spaces can squeeze more data through optical fibers and increase bandwidth. Moreover, by being able to control light at such small scales, optical devices can also be made more compact, requiring less energy to power them. But focusing light to such minute scales is inherently difficult. Once you reach sizes smaller than the wavelength of light—a few hundred nanometers in the case of visible light—you reach what's called the diffraction limit, and it's physically impossible to focus the light any further. But now the Caltech researchers, co-led by assistant professor of electrical engineering Hyuck Choo, have built a new kind of waveguide—a tunnellike device that channels light—that gets around this natural limit. The waveguide is made of amorphous silicon dioxide—which is similar to common glass—and is covered in a thin layer of gold. Just under two microns long, the device is a rectangular box that tapers to a point at one end.
Instead of focusing the light alone—which is impossible due to the diffraction limit—the new device focuses these coupled electron oscillations, called surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs). The SPPs travel through the waveguide and are focused as they go through the pointy end. Because the new device is built on a semiconductor chip with standard nanofabrication techniques, says Choo, the co-lead and the co-corresponding author of the paper, it is easy integrate with today's technology Previous on-chip nanofocusing devices were only able to focus light into a narrow line. They also were inefficient, typically focusing only a few percent of the incident photons, with the majority absorbed and scattered as they traveled through the devices. With the new device, light can ultimately be focused in three dimensions, producing a point a few nanometers across, and using half of the light that's sent through, Choo says. (Focusing the light into a slightly bigger spot, 14 by 80 nanometers in size, boosts the efficiency to 70 percent). The key feature behind the device's focusing ability and efficiency, he says, is its unique design and shape.
A field-effect transistor that may make graphene the next silicon has been developed by a University of Manchester team led by Nobel laureates Professor Andre Geim and Professor Konstantin Novoselov.
|
Researchers at Columbia University and University of California, San Diego, have introduced a novel "multi-messenger" approach to quantum physics that signifies a technological leap in how scientists can explore quantum materials. The findings appear in a recent article published in Nature Materials, led by A. S. McLeod, postdoctoral researcher, Columbia Nano Initiative, with co-authors Dmitri Basov and A. J. Millis at Columbia and R.A. Averitt at UC San Diego. "We have brought a technique from the inter-galactic scale down to the realm of the ultra-small," said Basov, Higgins Professor of Physics and Director of the Energy Frontier Research Center at Columbia. Equipped with multi-modal nanoscience tools we can now routinely go places no one thought would be possible as recently as five years ago." The work was inspired by "multi-messenger" astrophysics, which emerged during the last decade as a revolutionary technique for the study of distant phenomena like black hole mergers. Simultaneous measurements from instruments, including infrared, optical, X-ray and gravitational-wave telescopes can, taken together, deliver a physical picture greater than the sum of their individual parts. The search is now on for new materials that can supplement the current reliance on electronic semiconductors. Control over material properties using light can offer improved functionality, speed, flexibility and energy efficiency for next-generation computing platforms. Experimental papers on quantum materials have typically reported results obtained by using only one type of spectroscopy. The researchers have shown the power of using a combination of measurement techniques to simultaneously examine electrical and optical properties. The researchers performed their experiment by focusing laser light onto the sharp tip of a needle probe coated with magnetic material. When thin films of metal oxide are subject to a unique strain, ultra-fast light pulses can trigger the material to switch into an unexplored phase of nanometer-scale domains, and the change is reversible. By scanning the probe over the surface of their thin film sample, the researchers were able to trigger the change locally and simultaneously manipulate and record the electrical, magnetic and optical properties of these light-triggered domains with nanometer-scale precision. The study reveals how unanticipated properties can emerge in long-studied quantum materials at ultra-small scales when scientists tune them by strain. "It is relatively common to study these nano-phase materials with scanning probes. But this is the first time an optical nano-probe has been combined with simultaneous magnetic nano-imaging, and all at the very low temperatures where quantum materials show their merits," McLeod said. "Now, investigation of quantum materials by multi-modal nanoscience offers a means to close the loop on programs to engineer them."
A team led by researchers from the National University of Singapore has developed a method to enhance the photoluminescence efficiency of tungsten diselenide, a two-dimensional semiconductor, paving the way for the application of such semiconductors in advanced optoelectronic and photonic devices. Tungsten diselenide is a single-molecule-thick semiconductor that is part of an emerging class of materials called transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), which have the ability to convert light to electricity and vice versa, making them strong potential candidates for optoelectronic devices such as thin film solar cells, photodetectors flexible logic circuits and sensors. However, its atomically thin structure reduces its absorption and photoluminescence properties, thereby limiting its practical applications. By incorporating monolayers of tungsten diselenide onto gold substrates with nanosized trenches, the research team, led by Professor Andrew Wee of the Department of Physics at the NUS Faculty of Science, successfully enhanced the nanomaterial's photoluminescence by up to 20,000-fold. This technological breakthrough creates new opportunities of applying tungsten diselenide as a novel semiconductor material for advanced applications. Ms Wang Zhuo, a PhD candidate from the NUS Graduate School for Integrative Sciences and Engineering (NGS) and first author of the paper, explained, "This is the first work to demonstrate the use of gold plasmonic nanostructures to improve the photo-luminescence of tungsten diselenide, and we have managed to achieve an unprecedented enhancement of the light absorption and emission efficiency of this nanomaterial." Elaborating on the significance of the novel method, Prof Wee said, "The key to this work is the design of the gold plasmonic nanoarray templates. In our system, the resonances can be tuned to be matched with the pump laser wavelength by varying the pitch of the structures. This is critical for plasmon coupling with light to achieve optimal field confinement."
Via Mariaschnee
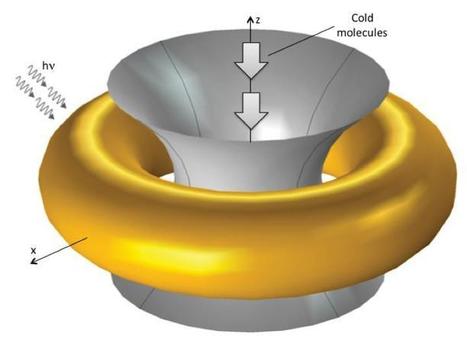
In a paper published in Physical Review A, Oak Ridge National Laboratory and University of Tennessee physicists describe conceptually how they may be able to trap and exploit a molecule’s energy to advance a number of fields. “A single molecule has many degrees of freedom, or ways of expressing its energy and dynamics, including vibrations, rotations and translations,” said Ali Passian of Oak Ridge National Lab. “For years, physicists have searched for ways to take advantage of these molecular states, including how they could be used in high-precision instruments or as an information storage device for applications such as quantum computing.”
Catching a molecule with minimal disturbance is not an easy task, considering its size — about 1 nanometer — but this paper proposes a method that may overcome that obstacle. When interacting with laser light, the ring toroidal nanostructure can trap the slower molecules at its center. That’s because the nano-trap, which can be made of gold using conventional nanofabrication techniques, creates a highly localized force field surrounding the molecules. The team envisions using scanning probe microscopy techniques, which can measure extremely small forces, to access individual nano-traps.
“Once trapped, we can interrogate the molecules for their spectroscopic and electromagnetic properties and study them in isolation without disturbance from the neighboring molecules,” Passian said.
Previous demonstrations of trapping molecules have relied on large systems to confine charged particles such as single ions. Next, the researchers plan to build actual nanotraps and conduct experiments to determine the feasibility of fabricating a large number of traps on a single chip. “If successful, these experiments could help enable information storage and processing devices that greatly exceed what we have today, thus bringing us closer to the realization of quantum computers,” Passian said.
Research engineers at MIT have developed a novel solar material in the form of a 2D metallic, dielectric photonic crystal. The material has remarkable properties of broadband absorption of sunlight, from visible to near infrared portions of the spectrum, with little dependence on the angle of the incident light. Efficiencies in these bands were measured to be 85% absorption of photons. The material also withstands temperatures up to 1000 degrees Celsius, making it suitable to act as the material for a collector of concentrated sunlight. Experiments show that the absorption is governed by the nanocavities. Tuning the absorption bands is accomplished simply by varying the radii and depths of the cavities.
The new material works as a part of the solar-thermophotovoltaic (STPV) device in which incident solar radiation is converted to infrared, heat energy, causing the material to emit light that is in turn converted to electrical energy. Earlier STPV devices contained nanocavities but were hollow and not filled with a dielectric. According to the primary author, “They were empty, there was air inside. No one had tried putting a dielectric material inside, so we tried that and saw some interesting properties.” A dielectric is a material which responds to electric fields by shielding or attenuating it via non-mobile charges, in contrast to a conductor which shields by rearrangement of electrons.
The cavities are sized in the right way such that there is a rich and complex absorption mode structure perfect for relevant wavelengths. “You can tune the absorption just by changing the size of the nanocavities,” said Dr. Chou.
Importantly, the new material is compatible with many kinds of existing manufacturing technologies. The lead author Dr. Chou said “This is the first-ever device of this kind that can be fabricated with a method based on current techniques, which means it’s able to be manufactured on silicon wafer scales.”
Prior work on similar materials were restricted in size to making devices that span only a few inches. The new cavity material is both cheaper and easier to process.
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) researchers have taken a big step towards miniaturizing magnetic data memory down to a single-atom bit: they fixed a single atom on a surface so the magnetic spin remained stable for ten minutes. “A single atom fixed to a substrate is [typically] so sensitive that its magnetic orientation is stable only for less than a microsecond,” said Wulf Wulfhekel of KIT. A compound of several million atoms has been needed to stabilize a magnetic bit longer than that. That’s because the magnetic moments of these atoms are normally easily destabilized by interactions with electrons, nuclear spins, and lattice vibrations of the substrate. The finding opens up the possibility of designing more compact computer memories and could also be the basis for quantum computers, Wulfhekel said. In their experiment, the researchers placed a single holmium atom onto a platinum substrate. At temperatures close to absolute zero (about 1 degree Kelvin), the atom was nearly vibration-free. They measured the magnetic orientation of the atom using the fine tip of a scanning tunneling microscope. The magnetic spin changed after about 10 minutes — “about a billion times longer than that of comparable atomic systems,” Wulfhekel said.
Reference: Toshio Miyamachi et al., Stabilizing the magnetic moment of single holmium atoms by symmetry, Nature, 2013, DOI: 10.1038/nature12759
In a report published in Nature Communications, a University of Manchester team led by Dr Irina Grigorieva shows how to create elementary magnetic moments in graphene and then switch them on and off.
This is the first time magnetism itself has been toggled, rather than the magnetization direction being reversed. Modern society is unimaginable without the use of magnetic materials. They have become an integral part of electronic gadgets where devices including hard disks, memory chips and sensors employ miniature magnetic components. Each micro-magnet allows a bit of information (‘0’ or ‘1’) to be stored as two magnetization directions (‘north’ and ‘south’). This area of electronics is called spintronics.
Despite huge advances, a big disappointment of spintronics has so far been its inability to deliver active devices, in which switching between the north and south directions is done in a manner similar to that used in modern transistors. This situation may dramatically change due to the latest discovery.
Graphene is a chicken wire made of carbon atoms. It is possible to remove some of these atoms which results in microscopic holes called vacancies. The Manchester scientists have shown that electrons condense around these holes into small electronic clouds, and each of them behaves like a microscopic magnet carrying one unit of magnetism, spin.
Dr Grigorieva and her team have shown that the magnetic clouds can be controllably dissipated and then condensed back.
She explains: “This breakthrough allows us to work towards transistor-like devices in which information is written down by switching graphene between its magnetic and non-magnetic states. These states can be read out either in the conventional manner by pushing an electric current through or, even better, by using a spin flow. Such transistors have been a holy grail of spintronics.”
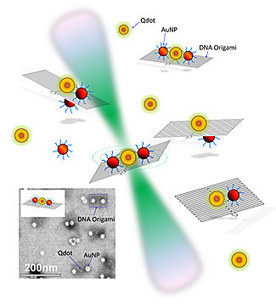
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have shown that by bringing gold nanoparticles close to the dots and using a DNA template to control the distances, the intensity of a quantum dot's fluorescence can be predictably increased or decreased. Their research was published in Angewandte Chemie. This breakthrough opens a potential path to using quantum dots as a component in better photodetectors, chemical sensors and nanoscale lasers. Anyone who has tried to tune a radio knows that moving their hands toward or away from the antenna can improve or ruin the reception. Although the reasons are well understood, controlling this strange effect is difficult, even with hundred-year-old radio technology. Similarly, nanotechnology researchers have been frustrated trying to control the light emitted from quantum dots, which brighten or dim with the proximity of other particles. The NIST team developed ways to accurately and precisely place different kinds of nanoparticles near each other and to measure the behavior of the resulting nanoscale constructs. Because nanoparticle-based inventions may require multiple types of particles to work together, it is crucial to have reliable methods to assemble them and to understand how they interact. The researchers looked at two types of nanoparticles, quantum dots, which glow with fluorescent light when illuminated, and gold nanoparticles, which have long been known to enhance the intensity of light around them. The two could work together to make nanoscale sensors built using rectangles of woven DNA strands, formed using a technique called "DNA origami."
Physicists at the University of New South Wales have created a transistor composed of a single atom, which is an amazing feat of nanoengineering, and could provide a better foundation for scalable quantum computing.
Via Jimi Paradise
A new ultrafast, nanoscale light-emitting diode (LED) device developed at Stanford’s School of Engineering transmits data at ultrafast rates while using 2,000 times less energy than laser-based systems in use today,” The nanophotonic device is a major step forward for on-chip data transmission, the researchers say. The device can transmit data at 10 gigabits per second. The researchers say it is a major step forward in providing a practical ultrafast, low-power, room-temperature light source for on-chip data transmission.
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...