Preclinical lupus encompasses a spectrum from enhanced SLE risk without clinical symptoms to individuals with autoantibodies and some SLE clinical features without meeting ACR classification. Studies have identified antibody and serological biomarkers years before disease onset. Incomplete lupus and undifferentiated connective tissue disease may occur during preclinical disease periods, but only 10–20% of these individuals transition to SLE and many have a mild disease course. Further studies are warranted to characterize biomarkers of early disease, identify individuals in need of close monitoring or preventive interventions, and elucidate mechanisms of disease pathogenesis without confounding factors of immunosuppressive medications or organ damage.
Via Krishan Maggon



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...

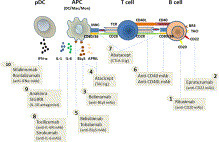







Volume 40, Issue 4, November 2014, Pages 621–635
Preclinical Rheumatic Disease
Preclinical Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Julie M. Robertson, PhDa, Judith A. James, MD, PhDa, b, c, d, , DOI: 10.1016/j.rdc.2014.07.004Bio markers have been elusive in SLE.